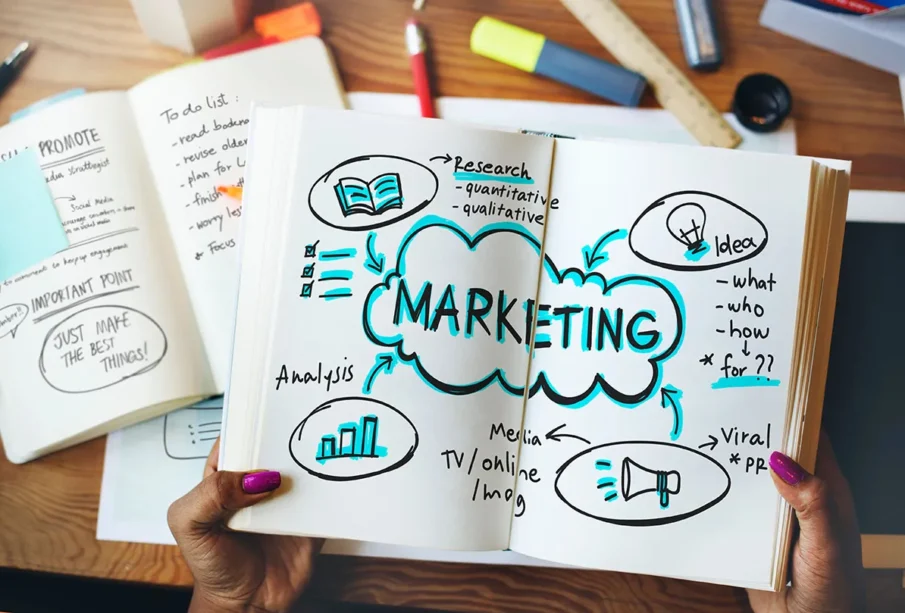
Introduction: More Than Just Selling
Marketing is often misunderstood as a mere act of selling products or services. In truth, it is a nuanced discipline that blends psychology, strategy, creativity, and data into an intricate dance of influence. A well-executed marketing campaign does not simply convince people to buy; it creates desire, shapes perceptions, and forges lasting connections between brands and audiences. It is the lifeblood of commerce, the bridge between supply and demand, and in today’s hyperconnected age, it is evolving faster than ever before.
The Evolution of Marketing: From Marketplace to Metaverse
The roots of marketing can be traced back to ancient marketplaces, where traders used persuasive words and eye-catching displays to draw customers. The industrial revolution transformed these rudimentary tactics into systematic approaches, giving rise to advertising, branding, and mass communication.
As the 20th century progressed, radio jingles, glossy magazine ads, and iconic television commercials dominated the landscape. Brands like Coca-Cola, Nike, and Apple mastered the art of storytelling, proving that products alone do not sell—stories do.
Today, we stand on the cusp of a digital frontier where marketing stretches beyond billboards and brochures into algorithms, social media feeds, and immersive virtual worlds.
Key Eras in Marketing History:
-
Pre-Industrial: Word-of-mouth, street hawkers, and local fairs.
-
Industrial Age: Print ads, product standardization, and mass production.
-
Post-War Era: Brand loyalty, celebrity endorsements, and television.
-
Digital Age: Internet advertising, social media, search engines.
-
Modern Era: Influencer marketing, data analytics, AI-driven personalization, and immersive experiences.
Each era builds on the last, adding layers of complexity while keeping the core principle intact—understanding people and connecting with them in meaningful ways.
The Pillars of Modern Marketing
While the channels and tools may have changed, the fundamental pillars of marketing endure. At its heart, marketing revolves around the “4 Ps”: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. In today’s context, some expand this to the “7 Ps,” adding People, Process, and Physical Evidence.
Core Pillars Explained:
-
Product: The good or service must solve a problem or fulfill a need better than alternatives.
-
Price: A delicate balance between value and profitability, shaped by perception and positioning.
-
Place: Ensuring the product is accessible where and when the customer wants it.
-
Promotion: The storytelling, advertising, and messaging that spark interest and drive action.
-
People: Everyone involved—from the brand’s employees to the customers themselves.
-
Process: The systems and workflows that ensure consistent delivery and customer satisfaction.
-
Physical Evidence: Tangible cues that reassure customers about what they are buying.
Every successful marketing strategy considers these elements in harmony, adjusting them to align with target audiences and market conditions.
The Power of Consumer Psychology
Great marketing is rooted in an understanding of how humans think, feel, and decide. Behavioral psychology, sociology, and cultural studies provide the backbone for effective campaigns. Why do we gravitate toward familiar logos? What makes a tagline stick? How do social norms and peer influence shape our choices?
Marketers use these insights to craft compelling narratives that tap into universal emotions—joy, fear, desire, nostalgia. The best campaigns feel less like a pitch and more like an invitation to belong to something bigger.
Psychological Triggers in Marketing:
-
Scarcity: Limited editions create urgency.
-
Social Proof: Testimonials and user reviews build trust.
-
Authority: Expert endorsements lend credibility.
-
Reciprocity: Free trials or samples encourage reciprocation through purchases.
-
Emotion: Stories that tug at the heart often outshine logic-driven pitches.
Understanding these principles allows marketers to design messages that resonate on a deeper level.
Digital Marketing: Where Data Meets Creativity
In the digital era, marketing is equal parts art and science. Technology enables brands to reach audiences with pinpoint accuracy, but it also demands a deft hand to avoid the noise and fatigue of constant online bombardment.
Key Aspects of Digital Marketing:
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Helping content rank higher on Google to attract organic traffic.
-
Content Marketing: Blogs, videos, podcasts—informative and entertaining content that nurtures trust.
-
Social Media Marketing: Engaging directly with audiences where they spend time—Instagram, X (formerly Twitter), LinkedIn, TikTok.
-
Email Marketing: Personalized messages that keep customers informed and loyal.
-
Pay-Per-Click Advertising (PPC): Targeted ads that drive immediate traffic and conversions.
-
Analytics: Tracking user behavior to refine strategies and measure ROI.
What distinguishes exceptional digital marketing is not just the technology but the human touch—brands that listen, respond, and adapt in real time earn enduring loyalty.
The Rise of Influencer and Experiential Marketing
In recent years, traditional advertising has taken a back seat to more authentic, immersive forms of marketing. Consumers are savvy—they crave genuine connections, not sales pitches. Enter influencer marketing, where trusted individuals become brand ambassadors, weaving products seamlessly into their lives.
Similarly, experiential marketing invites consumers to interact with a brand firsthand—pop-up stores, interactive installations, and virtual experiences that transform passive audiences into active participants.
Benefits of Modern Engagement:
-
Builds deeper emotional connections.
-
Generates organic buzz and user-generated content.
-
Fosters communities that advocate for the brand.
Ethics and Responsibility in Modern Marketing
Marketing holds immense power—it can shape public opinion, drive social trends, and even influence elections. With such influence comes responsibility. Misleading ads, data misuse, and manipulative tactics erode trust and can cause lasting harm to consumers and society.
Principles for Ethical Marketing:
-
Be truthful and transparent in all claims.
-
Respect privacy and handle data responsibly.
-
Promote diversity and inclusivity.
-
Avoid exploiting vulnerabilities or fear.
Brands that stand for integrity not only build stronger reputations but also inspire loyalty that withstands the test of time.
Conclusion: Marketing as an Ever-Evolving Craft
Marketing is not static—it reinvents itself with every technological breakthrough and cultural shift. It is a discipline that demands both left-brain logic and right-brain creativity, backed by a profound respect for the people it seeks to engage.
In a world flooded with noise, great marketing does not shout the loudest; it speaks clearly, honestly, and with purpose. It understands its audience, honors their time, and delivers value beyond the transaction.
As we navigate the future—augmented reality, AI-generated content, the metaverse—one truth remains unchanged: marketing will always be about people. It is the art of understanding human hearts and minds and the science of turning that understanding into meaningful connections that drive businesses forward and enrich lives in the process.
-
Your guide to purchasing custom cardboard boxes
November 30, 2021 -
The Nightlife in Queen Alba – Check out
January 28, 2022 -
Organizations – Some of the Basics
July 18, 2020
Latest Posts
-
What sustainable materials are used for gift cards?
July 20, 2025
Recent Posts
- What sustainable materials are used for gift cards? July 20, 2025
- Transforming Spaces: The Importance of Professional Strip-Out Services July 16, 2025
- The Symphony of Creation: Unveiling the Intricate World of Productions July 10, 2025
- The Art and Science of Influence: Decoding the Dynamic World of Marketing July 1, 2025
- Industry Unveiled: The Silent Engine Powering Modern Civilization June 10, 2025